Scientific Definition Of Buffer Capacity
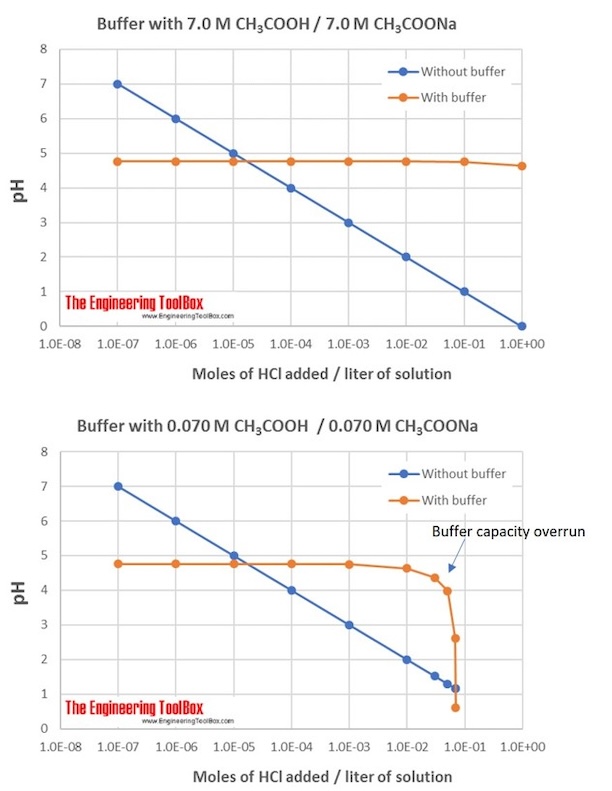
Definition 1 The buffer capacity of a solution is the amount in mol of strong acid or strong base that must be added to one liter of solution to change either the pH or pOH by one unit. Buffer capacity is a property of a buffer and it tells you how much acid or base you can add before the pH starts changing.
 How To Calculate Intrinsic Buffer Capacity
How To Calculate Intrinsic Buffer Capacity
Solutions with a weaker base have more buffer capacity when adding a strong acid.

Scientific definition of buffer capacity. That on which something stands. The buffering capacity of an anaerobic digester is determined by the amount of alkalinity present in the system. To elaborate if we take acid or base and add it to a buffer system there will be a change in the pH.
It is a unitless number. The relative ability of a buffer solution to resist pH change upon addition of an acid or a base. Buffer in chemistry solution usually containing an acid and a base or a salt that tends to maintain a constant hydrogen ion concentration.
The buffer capacity is a quantity in resisting the pH change at the time of addition of an acid or base. The solution either absorbs or removes H and OH- ions. The buffer capacity can also be defined as the amount of mole of strong base needed to change the pH of 1 L of solution by 1 pH of unit.
Therefore we first derive an expression for the buffer. Buffer base synonyms buffer base pronunciation buffer base translation English dictionary definition of buffer base. The bicarbonate ion HCO 3 is the main source of buffering capacity to maintain the systems pH in the range of 6576.
It has the property that the pH of the solution changes very little when a small amount of acid or base is added to it because of the following reactions. Basically as your buffer capacity goes up which Im going to abbreviate BC as your buffer capacity goes up you can add more of your acid or base before the pH starts changing a lot. Buffer capacity can be defined as the ability of a solution to resist rapid changes in pH.
A buffer consists of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. A buffer resists changes in pH due to the addition of an acid or base though consumption of the buffer. Where n is some equivalents of added strong base per 1 L of the solution.
Want to thank TFD for its existence. By definition a buffer system is a solution that resists a change in pH when acids or bases are added. The change can be either large or small.
Ions are atoms or molecules that have lost or gained one or more electrons. So to give a more clear definition buffer capacity may be defined as the quantity of a strong acid or strong base that must be added to one liter of a solution to change it by one pH unit. This video discusses the definition of buffer capacity and how to use that definition to answer questions related to comparing the buffer capacity of various.
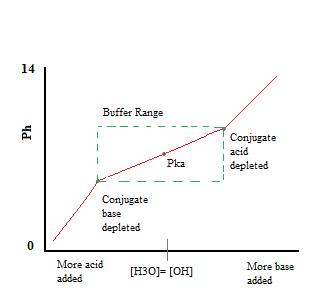
Note that the addition of n moles of acid will change the pH by the same value but in the opposite direction. The buffer capacity equation is as follows. For a buffer solution an acid with a pKa value close to the buffer solution itself should be chosen which ensures that each part of the conjugate base-acid pair is close to equal.
4 where represents the acidic strength of HA. To begin the derivation consider the Henderson-Hasselbalch representation for eqs 1 and 2. Buffer capacity A measure of the resistance of a buffer solution to pH change upon addition or removal of hydroxide ions.
An example of a common buffer is a solution of acetic acid CH3COOH and sodium. Buffer capacity β is defined as the moles of an acid or base necessary to change the pH of a solution by 1 divided by the pH change and the volume of buffer in liters. The higher the acid concentration of the buffer then the buffer capacity will be higher as well.
Buffer capacity is the amount of acid that buffers are capable of absorbing prior to breaking the capacity for adding strong acid. A buffer is an aqueous solution used to keep the pH of a solution nearly constant. A general buffer capacity estimate is 40 percent of the total sum of the molarites of the conjugate base and acid.
The concentration of HCO 3 in solution is related to the percent of carbon dioxide in the gas phase. Solutions with higher amounts of weak acid have higher levels of buffer capacity when adding a strong base. Buffer capacity A buffer solution is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base HA A or a weak base and its conjugate acid B BH.
2012 Farlex Inc. Buffering capacity is defined as the number of moles of strong base or acid needed to change the pH of a liter of buffer solution by one unit. Acidic solutions contain high concentrations of hydrogen ions H and have pH values less.
Buffer capacity is the amount of acid or base that can be added before the pH of a buffer changes. The buffer capacity of a mixture of reactants can be obtained from a superposition of the buffer capacities of individual reactants 44. Place the vase on the base.
 Introduction To Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
Introduction To Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
 Buffer Solution Ph Calculations Video Khan Academy
Buffer Solution Ph Calculations Video Khan Academy
 Of The Following Solutions Which Has The Clutch Prep
Of The Following Solutions Which Has The Clutch Prep
 Buffer Capacity Osu Chemistry Reel Program
Buffer Capacity Osu Chemistry Reel Program
 Pdf Understanding Deriving And Computing Buffer Capacity
Pdf Understanding Deriving And Computing Buffer Capacity
 Buffering Capacity An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Buffering Capacity An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Surface Ocean Ph And Buffer Capacity
Surface Ocean Ph And Buffer Capacity
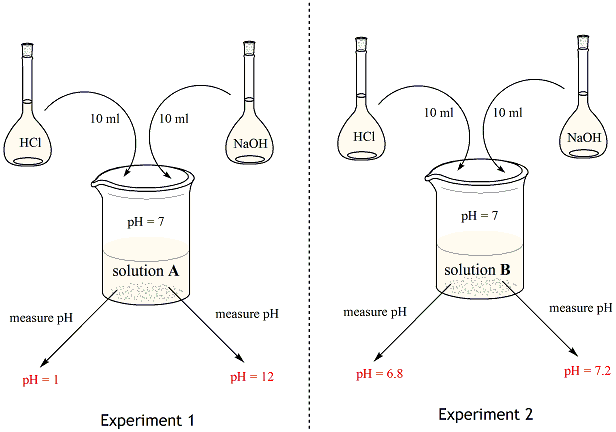 Chemistry Of Buffers And Buffers In Our Blood Article Khan Academy
Chemistry Of Buffers And Buffers In Our Blood Article Khan Academy
 Ionic Compound Science Flashcards Ionic Compound Science Student
Ionic Compound Science Flashcards Ionic Compound Science Student
 Buffer Choice For Hplc Separations
Buffer Choice For Hplc Separations
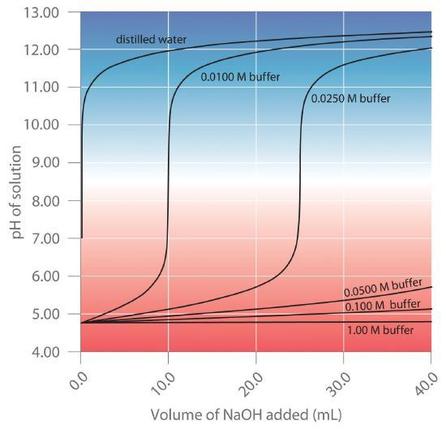 8 9 Buffer Capacity And Buffer Range Chemistry Libretexts
8 9 Buffer Capacity And Buffer Range Chemistry Libretexts
 What Is Kraljic Matrix Definition Model Example In 2020 Business Process Matrix Definitions
What Is Kraljic Matrix Definition Model Example In 2020 Business Process Matrix Definitions
 What Is A Biological Buffer And How To Choose The Best Buffer For Your Experiment Goldbio
What Is A Biological Buffer And How To Choose The Best Buffer For Your Experiment Goldbio