Buffer Capacity Chemistry Meaning
If you add an acid or a base to a buffered solution its pH will not change significantly. Buffer capacity can be also defined as quantity of strong acid or base that must be added to change the pH of one liter of solution by one pH unit.
The buffer capacity is numerically expressed to be equal with the minimum concentration of strong acid or strong base which causes the variation of buffers pH with one unit.
Buffer capacity chemistry meaning. For a given buffer solution there is a working pH range and a defined amount of acid or base that can be neutralized before the pH changes. The buffer capacity is exceeded when the number of moles of H or OH that are added to the buffer exceeds the number of moles of the buffer components. Personally the first time I let the liquid percolate at the bottom of the glass flask patiently waiting for the solution to turn to a tinge of pink or magenta it honestly made me feel like a scientist.
The buffer capacity is the amount of acid or base that can be added to a buffer solution before a large change in pH occurs. An example of a buffer solution is bicarbonate in blood which maintains the bodys internal pH. Buffer capacity is the measure of the efficiency of the buffers.
This video discusses the definition of buffer capacity and how to use that definition to answer questions related to comparing the buffer capacity of various. It is expressed as the amount of strong acid or base that must be added to 1 liter of the solution to change its pH by one unit. An example of a common buffer is a solution of acetic acid CH 3 COOH and sodium acetate.
Buffer in chemistry solution usually containing an acid and a base or a salt that tends to maintain a constant hydrogen ion concentration. If you remember high school chemistry or took a college course like Chemistry 101 you will have conducted a titration test. The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation can be used to measure the approximate pH of a buffer.
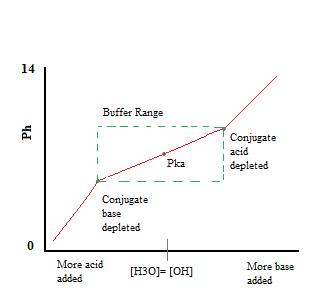
The higher the acid concentration of the buffer then the buffer capacity will be higher as well. The amount of acid or base that can be added to a buffer before changing its pH is called its buffer capacity. The buffering region is about 1 pH unit on either side of the pK a of the conjugate acid.
It can be defined as follows. A buffer consists of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. The Buffer Capacity is a measure of resistant a particular solution is resistant to change in pH when an acid or a base is added to it.
There are two key terms associated with buffers. A buffer is an aqueous solution that has a highly stable pH. The buffer capacity is used in the quantitative chemical analysis and the buffer index in studying biological systems.
Such definition - although have its practical applications - gives different values of buffer capacity for acid addition and for base addition unless buffer is equimolar and its pHpK a. Buffer capacity is the amount of acid or base that can be added before the pH of a buffer changes. Basically as your buffer capacity goes up which Im going to abbreviate BC as your buffer capacity goes up you can add more of your acid or base before the pH starts changing a lot.
A buffer resists changes in pH due to the addition of an acid or base though consumption of the buffer. A buffering agent is a weak acid or weak base that helps maintain the pH of an aqueous solution after adding another acid or base. It is a unitless number.
Buffer capacity refers to the amount of strong acid or base a buffer solution can take before significant pH changes take place. It can be also defined as the quantity of strong acid or base that must be added to change the pH of one liter of solution by one pH unit. Here we are going to learn about buffer capacity chemistry definition and formula.
Buffer capacity is a property of a buffer and it tells you how much acid or base you can add before the pH starts changing. Buffer capacity β is defined as the moles of an acid or base necessary to change the pH of a solution by 1 divided by the pH change and the volume of buffer in liters. Ions are atoms or molecules that have lost or gained one or more electrons.
The buffer capacity is a quantity in resisting the pH change at the time of addition of an acid or base. The field of application of both notions is different. The buffer capacity can also be defined as the amount of mole of strong base needed to change the pH of 1 L of solution by 1 pH of unit.
It is a measure of the resistance of a buffer solution to pH change on the addition of hydroxide ions. In Chemistry Buffers are compounds that are used to resist changes in pH of a solution when the acids or bases are added. A titration curve visually demonstrates buffer capacity where the middle part of the curve is flat because the addition of base or acid does not affect the pH of the solution drastically.
Buffer Capacity Buffers are characterized by the pH range over which they can maintain a more or less constant pH and by their buffer capacity the amount of strong acid or base that can be absorbed before the pH changes significantly. Buffer capacity is a quantitative measure of the resistance to change of pH of a solution by camerino italy containing a buffering agent with respect to a change of acid or alkali concentration. The buffer capacity is the amount of acid or base that can be added before the pH begins to change significantly.
β d C b d p H displaystyle beta frac dC_ b d mathrm pH where.
 Buffer Solution Acidic Buffer Basic Buffer Animation Buffer Solution Electron Configuration Solutions
Buffer Solution Acidic Buffer Basic Buffer Animation Buffer Solution Electron Configuration Solutions
 Buffer Capacity Chemistry Definition And Formula Az Chemistry
Buffer Capacity Chemistry Definition And Formula Az Chemistry
 Chemistry Of Buffers And Buffers In Our Blood Article Khan Academy
Chemistry Of Buffers And Buffers In Our Blood Article Khan Academy
 Digital Kemistry Best Chemistry Animated Blogs What Is Valency In Chemistry Definition Example 11th Chemistry Chemistry Biochemistry
Digital Kemistry Best Chemistry Animated Blogs What Is Valency In Chemistry Definition Example 11th Chemistry Chemistry Biochemistry
 Ionic Equilibrium L 5 Buffer Capacity Definition And Calculation Jee Mains Chemistry Class 11 Youtube
Ionic Equilibrium L 5 Buffer Capacity Definition And Calculation Jee Mains Chemistry Class 11 Youtube
 Introduction To Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
Introduction To Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
 Hybridization Short Tricks How To Find The Shape Of Molecule Using Hybridisation Molecules Cool Gifs Hindi
Hybridization Short Tricks How To Find The Shape Of Molecule Using Hybridisation Molecules Cool Gifs Hindi
 Understanding Cec Buffer Soil Ph Percent Saturation Soil Ph Soil Soil Texture
Understanding Cec Buffer Soil Ph Percent Saturation Soil Ph Soil Soil Texture
 What Is Buffer Capacity Youtube
What Is Buffer Capacity Youtube
 Cec Stuff To Internalize Or Project Onto Something Already Known Nrem Soils Soil Health Humus Soil Composting Process
Cec Stuff To Internalize Or Project Onto Something Already Known Nrem Soils Soil Health Humus Soil Composting Process
 Pin By Integrated Learning Strategies On Ots Pts And Professionals Social Work Exam Social Work Theories Counseling Psychology
Pin By Integrated Learning Strategies On Ots Pts And Professionals Social Work Exam Social Work Theories Counseling Psychology
 Buffer Capacity Video Buffer Solutions Khan Academy
Buffer Capacity Video Buffer Solutions Khan Academy
 Buffer Capacity Osu Chemistry Reel Program
Buffer Capacity Osu Chemistry Reel Program
 What Is Buffer Capacity And What Is The Condition For Maximum Buffer Capacity Youtube
What Is Buffer Capacity And What Is The Condition For Maximum Buffer Capacity Youtube
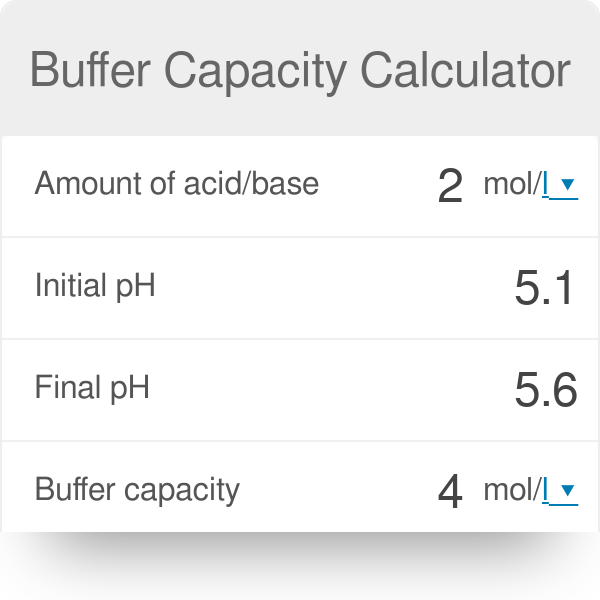 How To Calculate Buffer Capacity
How To Calculate Buffer Capacity
 Equilibrium Constant Relationship Kp Kc Kx Kn Giao Dục
Equilibrium Constant Relationship Kp Kc Kx Kn Giao Dục
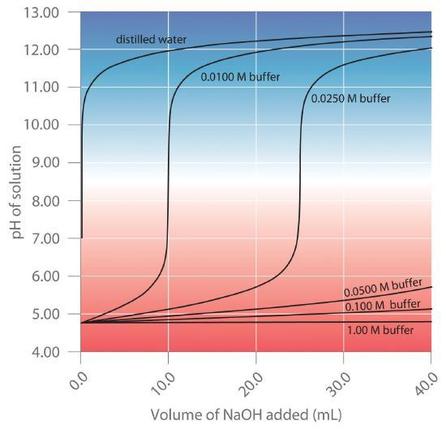 8 9 Buffer Capacity And Buffer Range Chemistry Libretexts
8 9 Buffer Capacity And Buffer Range Chemistry Libretexts